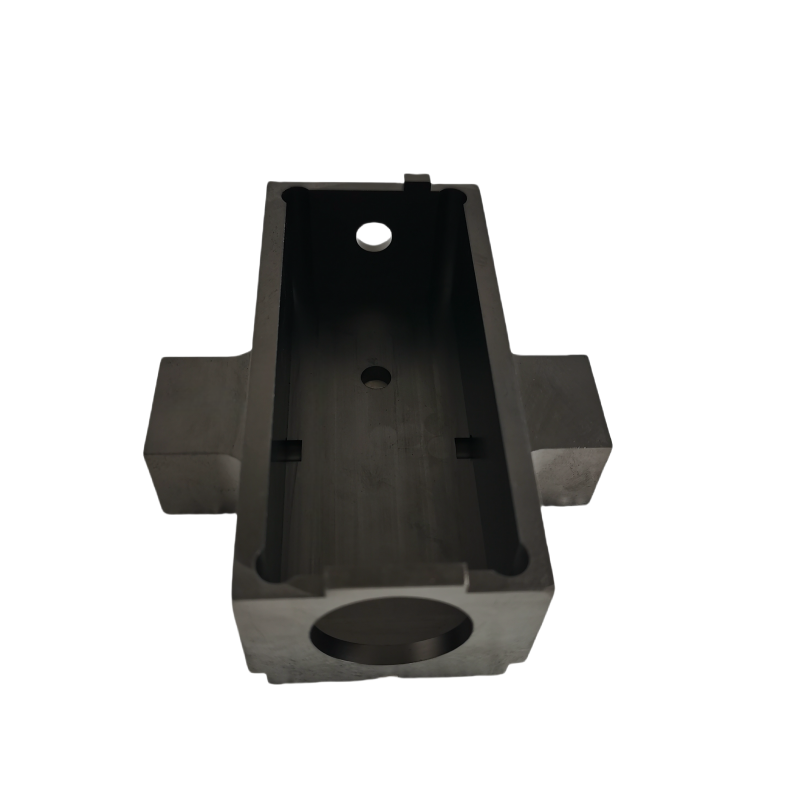
In today's demanding industrial landscape, achieving precise temperature control while maintaining energy efficiency has become a critical factor for manufacturing success. Graphite heaters have emerged as a superior heating solution, offering exceptional performance characteristics that surpass traditional heating elements in numerous applications. These advanced heating systems deliver consistent thermal output while providing remarkable durability and cost-effectiveness across various industrial processes.
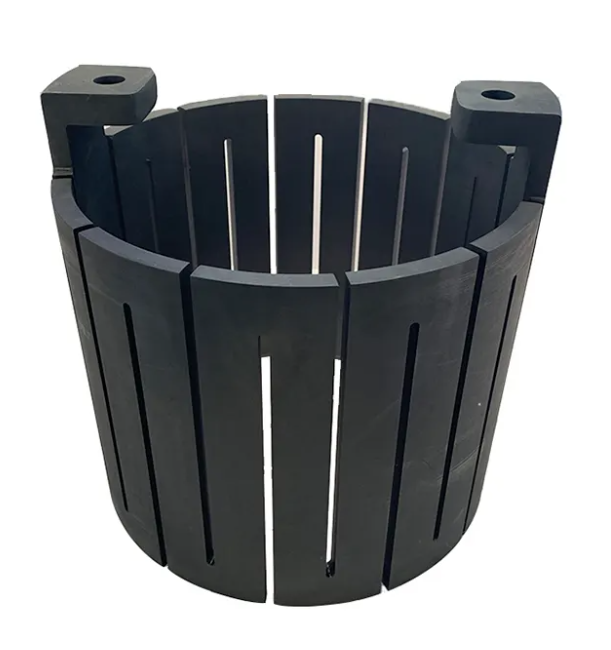

Superior Thermal Performance Characteristics
Exceptional Heat Transfer Efficiency
The fundamental advantage of graphite heaters lies in their extraordinary thermal conductivity properties. Unlike conventional heating elements, graphite materials exhibit thermal conductivity values ranging from 100 to 400 W/mK, depending on the grade and manufacturing process. This exceptional heat transfer capability ensures rapid temperature response and uniform heat distribution across the heating surface, eliminating hot spots that can compromise product quality in sensitive manufacturing processes.
The crystalline structure of graphite enables efficient phonon transport, which translates to superior heat dissipation characteristics. This property becomes particularly valuable in applications requiring precise temperature control, such as semiconductor manufacturing, metal processing, and advanced materials production. The enhanced thermal performance directly contributes to improved process efficiency and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional resistance heating elements.
Rapid Temperature Response
Manufacturing processes often require quick temperature adjustments to maintain optimal conditions and respond to process variations. Graphite heaters demonstrate remarkable thermal responsiveness, achieving target temperatures significantly faster than ceramic or metallic heating elements. This rapid response capability stems from the low thermal mass and high thermal diffusivity of graphite materials, enabling precise temperature control in dynamic operating environments.
The quick heating and cooling cycles possible with graphite heaters prove especially beneficial in batch processing applications where temperature cycling is frequent. Industries such as glass manufacturing, metal heat treatment, and chemical processing benefit significantly from this enhanced thermal agility, resulting in improved production throughput and reduced cycle times.
Enhanced Durability and Longevity
Chemical Resistance Properties
Industrial heating applications often involve exposure to corrosive chemicals, reactive gases, and harsh environmental conditions that can rapidly degrade conventional heating elements. Graphite heaters exhibit exceptional chemical inertness, remaining stable in the presence of most acids, bases, and organic solvents. This chemical resistance extends the operational lifespan of heating systems while maintaining consistent performance throughout extended service periods.
The inherent stability of graphite materials under chemical stress eliminates the need for frequent replacement and reduces maintenance costs associated with heating system failures. In applications involving aggressive chemical environments, such as semiconductor etching processes or chemical vapor deposition, graphite heaters maintain their structural integrity and heating performance where other materials would quickly deteriorate.
High Temperature Stability
Operating temperatures in industrial processes can reach extreme levels that challenge the limits of conventional heating materials. Graphite heaters demonstrate exceptional thermal stability, operating effectively at temperatures exceeding 3000°C in inert atmospheres. This high-temperature capability opens possibilities for applications in advanced materials processing, metal refining, and specialized manufacturing processes that require extreme thermal conditions.
The thermal expansion coefficient of graphite remains relatively low even at elevated temperatures, minimizing thermal stress and mechanical deformation that can affect heating uniformity. This dimensional stability ensures consistent performance throughout the operating temperature range, reducing the risk of thermal cycling fatigue that commonly affects other heating element materials.
Economic Advantages and Cost Effectiveness
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Energy costs represent a significant portion of industrial operating expenses, making energy-efficient heating solutions essential for maintaining competitive manufacturing operations. Graphite heaters convert electrical energy to thermal energy with exceptional efficiency, minimizing power consumption while delivering required thermal output. The high thermal conductivity and low thermal mass characteristics contribute to reduced energy waste and improved overall system efficiency.
Comparative studies demonstrate that graphite heaters can achieve energy savings of 20-30% compared to traditional heating elements in similar applications. These energy efficiency gains translate to substantial cost reductions over the operational lifetime of heating systems, providing compelling economic justification for adopting graphite heating technology in industrial applications.
Reduced Maintenance Requirements
The robust construction and chemical stability of graphite heaters significantly reduce maintenance requirements compared to conventional heating systems. The absence of oxidation issues, corrosion susceptibility, and thermal shock sensitivity means fewer unplanned shutdowns and reduced maintenance labor costs. This reliability becomes particularly valuable in continuous process operations where heating system failures can result in substantial production losses.
Extended service life characteristics of graphite heaters further enhance their economic value proposition. While initial investment costs may be higher than conventional alternatives, the total cost of ownership calculations typically favor graphite heating solutions due to reduced replacement frequency, lower maintenance costs, and improved energy efficiency over the system lifetime.
Industrial Applications and Versatility
Semiconductor Manufacturing Applications
The semiconductor industry demands precise temperature control and contamination-free processing environments that align perfectly with the capabilities of graphite heaters. These heating systems provide the uniform temperature distribution essential for consistent wafer processing while maintaining the chemical purity required for advanced semiconductor fabrication. The ability to operate in ultra-high vacuum conditions makes graphite heaters ideal for molecular beam epitaxy and other advanced deposition processes.
Rapid thermal processing applications in semiconductor manufacturing benefit significantly from the quick response characteristics of graphite heaters. The ability to achieve precise temperature ramps and maintain isothermal conditions across large substrate areas ensures optimal device characteristics and improved manufacturing yields. This precision control capability becomes increasingly important as semiconductor devices continue to shrink and performance requirements become more stringent.
Metal Processing and Heat Treatment
Metal processing operations require consistent heating performance across wide temperature ranges to achieve desired material properties and microstructures. Graphite heaters excel in applications such as vacuum heat treatment, powder metallurgy sintering, and specialized alloy processing where precise temperature control and contamination prevention are critical. The ability to operate in inert or reducing atmospheres without degradation makes these heating systems particularly suitable for reactive metal processing.
High-temperature brazing and welding applications benefit from the uniform heat distribution characteristics of graphite heaters, ensuring consistent joint quality and mechanical properties. The thermal responsiveness enables precise control of heating and cooling cycles, optimizing metallurgical transformations and minimizing thermal stress in processed components.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Environmental sustainability has become a paramount consideration in industrial operations, driving the adoption of energy-efficient technologies that minimize environmental impact. The superior energy efficiency of graphite heaters directly contributes to reduced carbon emissions by lowering electrical energy consumption for thermal processing applications. This environmental benefit aligns with corporate sustainability initiatives and regulatory requirements for emissions reduction.
The extended operational lifespan of graphite heaters reduces material waste associated with frequent heating element replacement, further contributing to environmental sustainability goals. The recyclability of graphite materials at end-of-life adds another dimension to the environmental advantages of these heating systems, supporting circular economy principles in industrial operations.
Process Emission Reduction
Traditional heating elements often contribute to process emissions through oxidation byproducts and material degradation during high-temperature operation. Graphite heaters operate without generating harmful emissions or contaminating byproducts, creating cleaner processing environments that benefit both worker safety and environmental compliance. This clean operation characteristic proves particularly valuable in applications where emission control is critical.
The chemical inertness of graphite materials prevents catalytic reactions that might generate unwanted chemical species during heating processes. This stability ensures that heating systems do not contribute to process contamination or environmental emissions, supporting cleaner production methods and regulatory compliance in environmentally sensitive applications.
FAQ
What temperature range can graphite heaters achieve
Graphite heaters can operate effectively across an extremely wide temperature range, from ambient conditions up to 3000°C in inert atmospheres. In oxidizing environments, the maximum operating temperature is typically limited to around 500°C to prevent oxidation. The specific temperature capability depends on the graphite grade, heater design, and atmospheric conditions, making them suitable for both moderate and extreme temperature applications.
How do graphite heaters compare to ceramic heating elements in terms of efficiency
Graphite heaters typically demonstrate 20-30% higher energy efficiency compared to ceramic heating elements due to their superior thermal conductivity and lower thermal mass. The rapid heat-up characteristics and uniform temperature distribution of graphite heaters result in reduced energy waste and improved process efficiency. Additionally, the longer service life of graphite heaters contributes to better overall cost-effectiveness despite potentially higher initial investment costs.
What maintenance is required for graphite heating systems
Graphite heaters require minimal maintenance due to their chemical inertness and structural stability. Routine maintenance typically involves periodic inspection for physical damage, cleaning of surfaces to remove any accumulated deposits, and verification of electrical connections. The absence of oxidation issues and corrosion susceptibility significantly reduces maintenance requirements compared to metallic heating elements, resulting in lower operational costs and improved system reliability.
Are graphite heaters suitable for use in vacuum applications
Yes, graphite heaters are exceptionally well-suited for vacuum applications due to their low outgassing characteristics and ability to maintain structural integrity under vacuum conditions. The material does not release volatile compounds that could contaminate vacuum processes, making them ideal for applications such as vacuum heat treatment, molecular beam epitaxy, and other ultra-high vacuum processes where contamination control is critical.