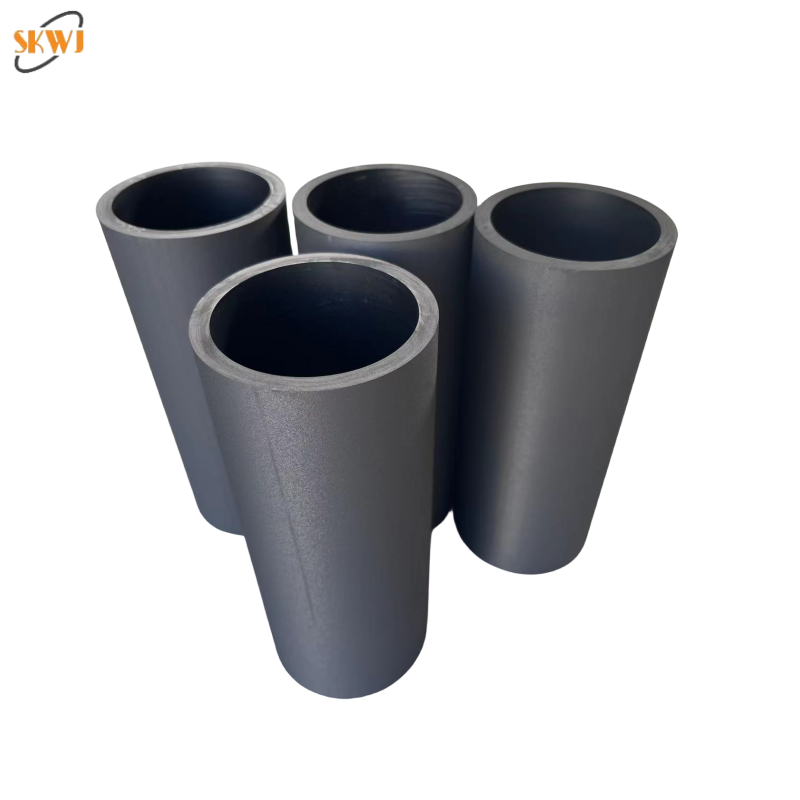
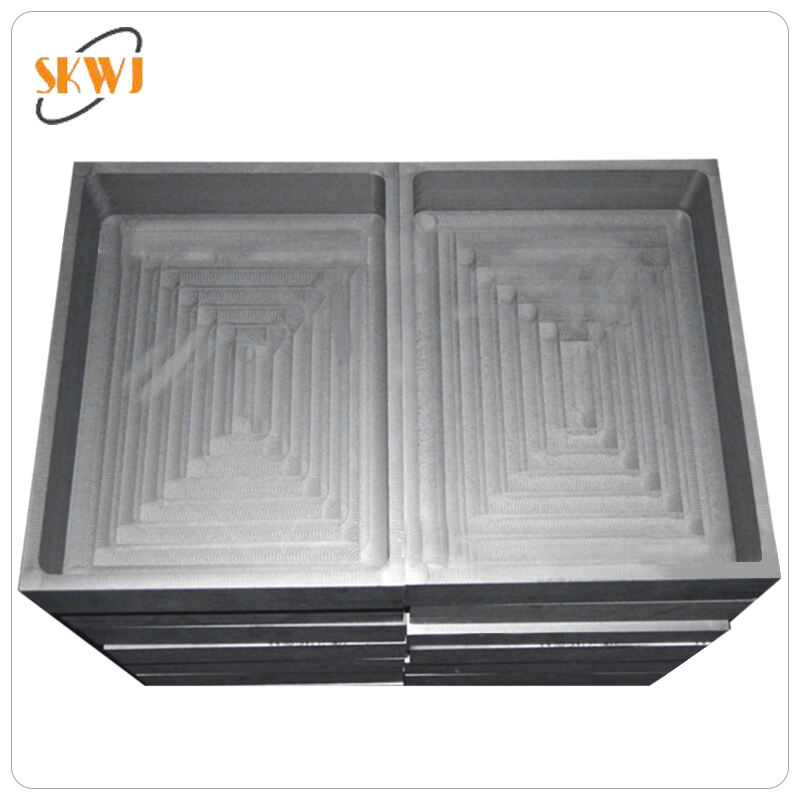
synthetic graphite production
Synthetic graphite production represents a sophisticated industrial process that transforms carbon-based raw materials into high-purity graphite through careful thermal treatment. This process involves heating petroleum coke or coal tar pitch to temperatures exceeding 2800°C, resulting in a highly crystalline carbon structure. The production method enables precise control over the final product's properties, including particle size, density, and electrical conductivity. The process begins with selecting and preparing raw materials, followed by primary processing steps such as calcination and grinding. The material then undergoes graphitization, where the atomic structure is transformed into the characteristic hexagonal crystalline arrangement of graphite. Quality control measures throughout the process ensure consistent product specifications. The resulting synthetic graphite finds extensive applications across various industries, from electric vehicle batteries and fuel cells to nuclear reactors and semiconductor manufacturing. Its superior purity and controlled properties make it essential for high-performance applications where natural graphite may not meet stringent requirements. The production process can be customized to create different grades of synthetic graphite, each optimized for specific applications, whether it's for electrodes, battery anodes, or thermal management systems.